Did you ever wonder is there any relationship between the Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy that you had learned in physics during your school days?
Some background knowledge:
Speed-time graph
Time to read this article: 5 ~ 7 minutes
In this blog we are going to explore this topic
Speed-time graph
Time to read this article: 5 ~ 7 minutes
In this blog we are going to explore this topic
First let us recap
Gravitational Potential Energy(g.p.e.) is:
Gravitational Potential Energy(g.p.e.) is:
m = mass in kg
h = height of the object above the ground(in meter)
h = height of the object above the ground(in meter)
Kinetic Energy(k.e.) is:
v = speed in m/s
Question:
Finding g.p.e
Step 1: draw speed-time graph
If we want to find the g.p.e we need to know the total distance traveled by the ball in 5 seconds.In simplicity we need to draw a speed-time graph, with the value of acceleration of free fall, as the following
at time t = 0, v = 0 m/s
at time t = 1, v = 10 m/s
at time t = 2, v = 20 m/s
at time t = 5, v = 50 m/s
The speed-time graph:
Step 2: find height,which is area under the curve from speed-time graph
Total distance is the area under the curve of speed-time graphthe final speed is 50 m/s , and the total time taken to reach the final speed is 5 seconds
by using the g.p.e ,
Finding k.e.
From the speed-time graph, we can also get the final velocity of the ball when the ball reach the ground which is 50 m/s
alternatively, since we know the velocity of the ball, we can now try to use the k.e. formulae to calculate its kinetic energy
Now you see, both computed k.e. and g.p.e are the same.
Math work out
let us use mathematical method to prove itEq1:
Step 1: Find formulae/representation to compute h
refer to the speed time graph, h is the area under the curveEq2:
v = final velocity at time t, which is 50m/s
t = total time taken to reach final velocity, which is 5 seconds
Step 2: Find formulae/representation to compute g
refer to the speed time graph, g (acceleration) is the gradient of that lineEq3:
from the speed time graph, we know that v0 = 0, and v1 = 50 m/s and it took a total of t = 5 seconds
so as to compare with the v in the Eq2 , we can equate them as
Eq4:
by substituting Eq4 into Eq3 we get Eq5:
Step 3: Prove left hand side Eq = right hand side Eq
Finally we substitute Eq5 and Eq2 into Eq1:the left hand side equation is equivalent to the right hand side equation
We know that the kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. It does not contain direction, however, the g.p.e is indicating force pointing downwards.
We can conclude that the kinetic energy in the context of force of gravity ,it is the absolute/magnitude representation of the g.p.e
About author: he is an online tutor which give guidance to student so that they are able to overcome their obstacles upon understanding physics and mathematics. If you are interested, please send an email to SimplyOvercomer@gmail.com.



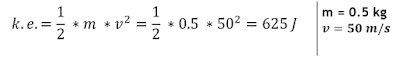


No comments:
Post a Comment